The review, published by an international group of researchers, argues that the mouth and liver are more connected than we thought.
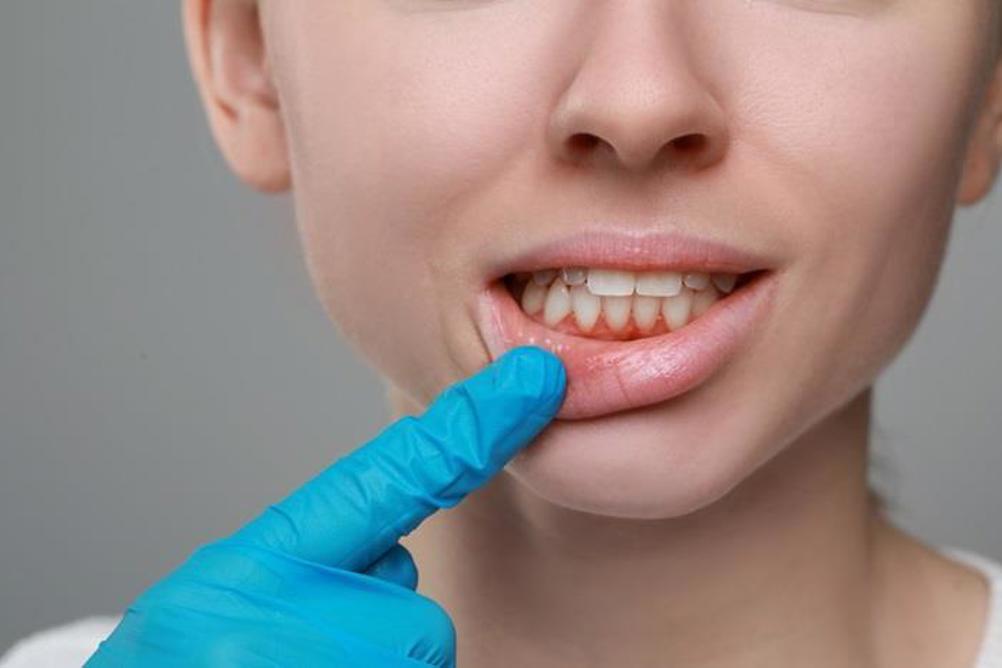
Gum disease, especially in its more advanced form known as periodontitis, is a chronic inflammatory condition caused by bacterial infections in the tissues that support the teeth. It is one of the most common diseases worldwide, and its severity tends to increase with age, smoking, alcohol use, and poor access to dental care. For patients already struggling with liver disease—many of whom share these same risk factors—oral health can often be neglected.
A hidden link
The review has laid out multiple ways that periodontitis may aggravate liver disease. The first is via the ‘oral-gut-liver axis’, a term researchers use to describe the complex interplay between oral bacteria, the gut microbiome, and liver function. Pathogenic bacteria from the mouth can be swallowed or enter the bloodstream during everyday activities like chewing and brushing. Once in the gut, these microbes may alter the composition of the intestinal microbiome, leading to dysbiosis and increased gut permeability—also known as a ‘leaky gut’. This can allow bacterial products such as endotoxins to reach the liver, triggering inflammation and fibrogenesis.
Register now to continue reading
Thank you for visiting Dental Nursing and reading some of our resources. To read more, please register today. You’ll enjoy the following great benefits:
What's included
-
Up to 2 free articles per month
-
New content available
Already have an account? Sign in here
